What Is the Conjugate Acid in an Acetate Buffer System
What is the definition of a basic buffer. HC2H3O2 acetic acid and its conjugate base the acetate Ion C2H3O2 with a minus 1 charge.
A buffer system can be made by mixing a soluble compound that contains the conjugate base with a solution of the acid such as sodium acetate with acetic acid or ammonia with ammonium chloride.

. An acidic buffer is a solution of a weak acid acetic acid and its conjugate base pair sodium acetate that prevents the pH of a solution from changing drastically through the action of each component with incoming acid or base. A buffers pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it. In the acetic acidacetate buffer Ka H x acetic acidacetate ion.
27 votes According to the Brønsted-Lowry acid-base theory a conjugated acid is the acid part of a pair of chemical species that are formed as a result of the ionization of an acid following the loss of a hydrogen ion. Both are in chemical equilibrium with each other. Acetic acid is an organic compound that helps to manufacture vinegar while acetate ion is.
OAc conjugate weak base. What is the purpose of NaCH3COO in the buffer. They are in a chemical equilibrium with each other.
Find an answer to your question What is the conjugate acid in an acetate buffer system. A buffer is an aqueous solution consisting of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The conjugate acid CH3COO.
And CH₃CO₂ acetate ion. An acetate buffer contains roughly equal concentrations of acetic acid and acetate ion. They resist a change in pH upon dilution or upon the addition of small amounts of acidalkali to them.
A buffer is a mixture of a weak base and its conjugate acid mixed together in appreciable concentrations. A buffer containing acetic acid and sodium acetate CH 3 COOH CH 3 COONa is an example of a weak acid and its salt. An acid buffer is a solution that contains roughly the same concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
CH3COOH aqH2O lH3O aqCH3COO. The key difference between acetic acid and acetate is that acetic acid is a neutral compound whereas acetate is an anion having a net negative electrical charge. And for buffers the Henderson-Hasselbalch equation applies.
Likewise if a bit of strong base is added to a portion of the buffer a bit of the weak acid acetic acid is converted to conjugate base acetate ion. PHpKa log OAc HOAc Thus with the Ka of acetic acid as 18 105 the pKa is logKa 476 and. Thus an acetate buffer contains roughly equal concentrations of acetic acid and acetate ion.
Buffer capacity depends on the amounts of the weak acid and its conjugate base that are in a buffer mixture. Brookelynn8597 brookelynn8597 07212015 Chemistry High School answered What is the conjugate acid in an acetate buffer system. What is a buffer system in chemistry example.
The first solution has more. A buffer solution can be obtained by dissolving an acid and its salt or a base and its salt. 7 rows The buffer action maintains steady pH by adjusting equilibrium between a weak acid or a weak.
What is the purpose of a buffer system. Two molecular entities differing only by a single proton. Equal concentrations of a weak base with its conjugate acid or addition of half an equiv of strong acid to weak base will generate a buffer.
Also what makes a buffer a good buffer. A buffer is an aqueous solution containing a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. The basic part that forms as a result of the transfer is called the conjugate base.
They act to moderate gross changes in pH. A buffer is simply a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Consider the acetic acid buffer system with acetic acid CH3COOH and its salt sodium acetate NaCH3COO.
For example 1 L of a solution that is 10 M in acetic acid and 10 M in sodium acetate has a greater buffer capacity than 1 L of a solution that is 010 M in acetic acid and 010 M in sodium acetate even though both solutions have the same pH. From the salt NaCH3COO is needed to neutralize any added base. When preparing an acetate buffer at pH 45 with 001 M solutions of acetic acid pKa 48 and sodium acetate the volume of acetic acid needed would be ____ the volume of sodium acetate solution.
It is used to prevent any change in the pH of a solution regardless of solute. To obtain a buffer solution a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid must be present in the solution at the same time in equilibrium with each other. The species created when a base accepts a proton.
Buffer Solution is a water solvent based solution which consists of a mixture containing a weak acid and the conjugate base of the weak acid or a weak base and the conjugate acid of the weak base. A buffer solution or a buffer is a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base or a mixture of a weak base and its conjugate acid. It is the ratio of acetic acid concentration to acetate ion concentration that controls the pH of the buffer.
The pH of a buffer consisting of 050 M CH 3 COOH and 050 M CH 3 COONa is 474. More than half of d. PH pKa log A HA The ratio of acetate to acetic acid is given by OAc HOAc.
A Buffer Is a Solution Containing a weak Acid and its conjugate base Ex. In practice a buffer solution contains either a weak acid and its conjugate base or a weak base and its conjugate acid. Buffers work by reacting with any added acid or base to control the pH.
As the above example shows a buffer works by replacing a strong acid or base with a weak one. About six times e. 10pHpKa OAc HOAc.
Acetic acid in the buffer solution will react with the addition of sodium hydroxide NaOH. CH₃CO₂H H₂O CH₃CO₂ H₃O where CH₃CO₂H - acetic acid. An acid buffer is a solution that contains roughly the same concentrations of a weak acid and its conjugate base.
Less than half of c. The above equation for K a can be rearranged to solve. One example of a buffer is a solution made of acetic acid the weak acid and sodium acetate the salt.
Why Is Acetic Acid And Sodium Acetate A Good Buffer Quora

Sch 4 U 1 What Are Buffers Buffers Are Mixtures Of Conjugate Acid Base Pairs That Allow A Solution To Resist Changes In Ph When Acids And Or Bases Ppt Download

A Qualitative Description Of Acid Base Equilibriums

You Have 250ml Of A 0 56m Solution Of Sodium Acetate How Many Ml Of 0 50m Acetic Acid Should Be Added To Make A Buffer Of Ph 4 40 Study Com

Buffer Solution Active Learning Instructional Sequence Part 1 Chemdemos
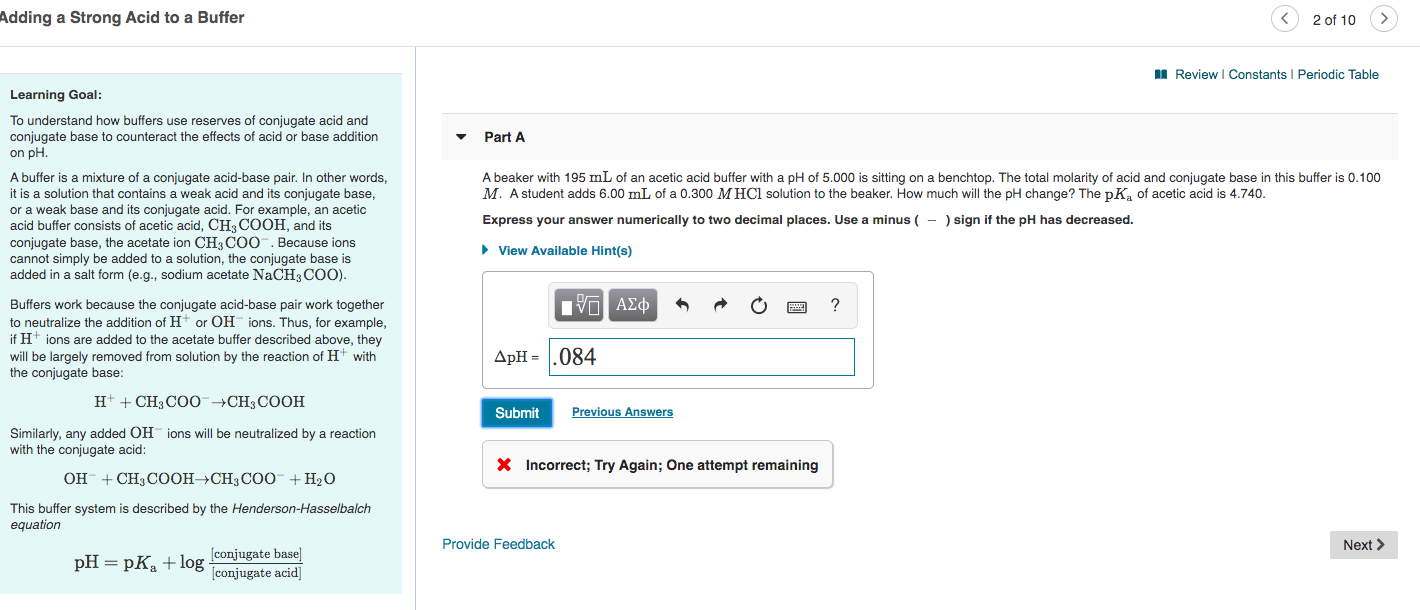
Solved To Understand How Buffers Use Reserves Of Conjugate Chegg Com
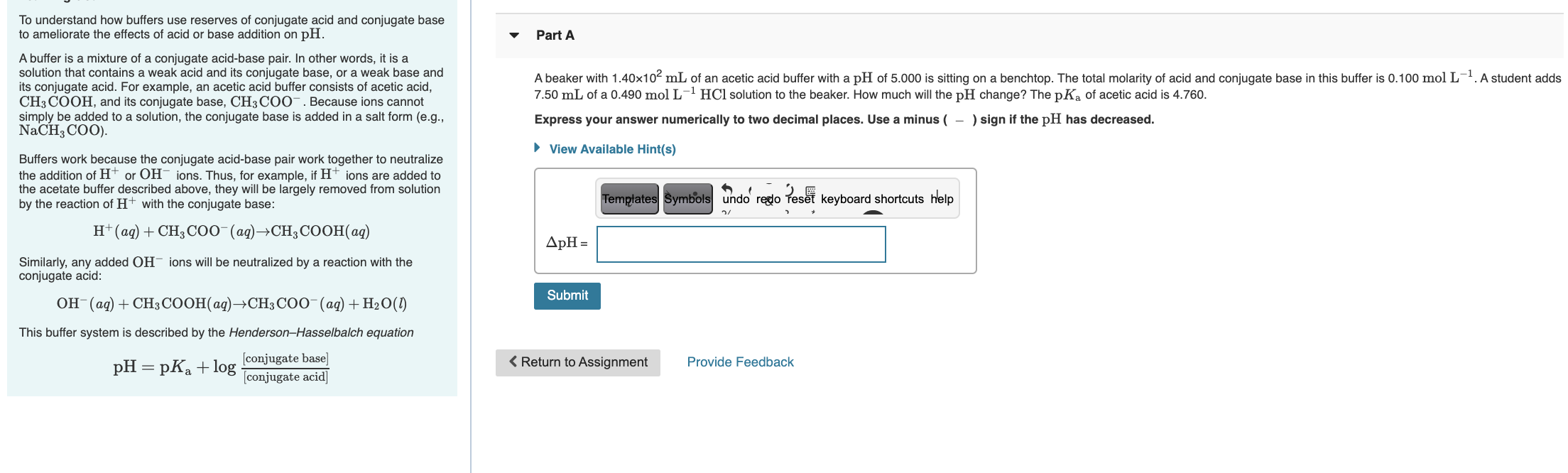
Solved Part A To Understand How Buffers Use Reserves Of Chegg Com

Chapter 8 Acids And Bases Ppt Download

Chapter 10 Acids And Bases Ppt Download

1 Chapter 10 Acids And Bases 10 9 Buffers 2 When An Acid Or Base Is Added To Water The Ph Changes Drastically A Buffer Solution Resists A Change In Ppt Download

Solved Buffers Work Because The Conjugate Acid Base Pair Work Together To Neutralize The Addition Of H Or Oh Ions Thus For Example If H Ions Are Added To The Acetate Buffer Described Above

Compare 1 L Of Acetate Buffer Solution 0 50 Mol Of Acetic Acid And
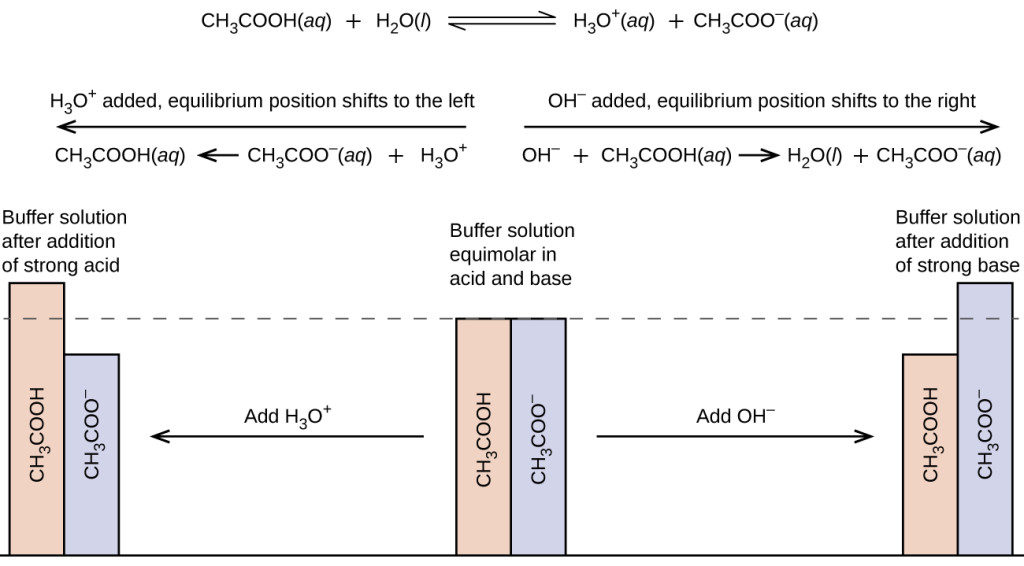
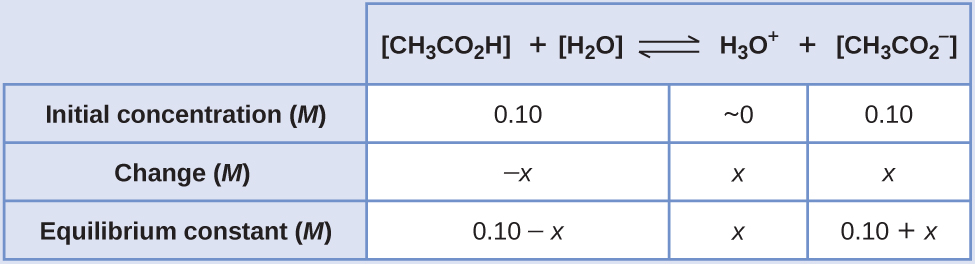





Comments
Post a Comment